Article Body
Introduction
Artificial intelligence is no longer just a futuristic concept—it's reshaping workplaces across the globe, automating tasks once done by humans. As AI's impact accelerates in 2025, many professionals are left wondering: Will my job survive, and if not, what should I learn to safeguard my career? This article delivers actionable insights for anyone looking to remain relevant and competitive as AI transforms employment landscapes.
Context & Background
Artificial intelligence has rapidly evolved, moving from scripted automation in factories to sophisticated systems capable of analyzing data, making decisions, and even writing code or content. Over the past decade, AI's role has expanded across sectors:
-
Manufacturing leverages robotics for precision and speed.
-
Healthcare uses AI for diagnostics and patient management.
-
Finance automates fraud detection and customer interactions.
The integration of machine learning and generative AI since the early 2020s has accelerated this shift, making more complex, cognitive tasks susceptible to automation.
The Main Event: How AI is Replacing Human Jobs
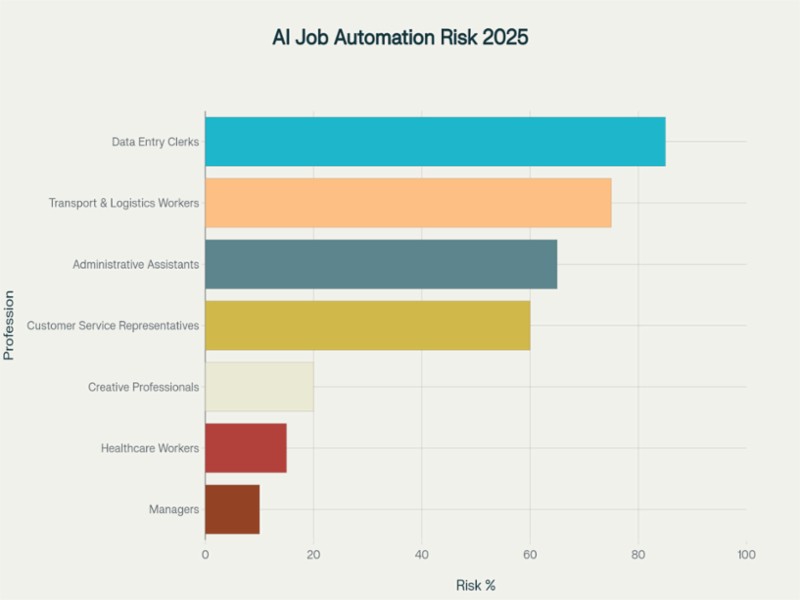
Automation has already replaced millions of routine, repetitive tasks—think assembly lines and data entry. In recent years, however, AI's reach has grown to include white-collar professions, from customer service chatbots to AI-driven attorneys reviewing legal contracts.
Recent studies predict that up to 30% of all current work activities could be automated by 2030, with sectors like transportation, logistics, and administrative services most at risk. Even creative fields are seeing the adoption of AI tools in content generation, design, and music production.
Analysis & Implications: What to Learn to Keep Your Job
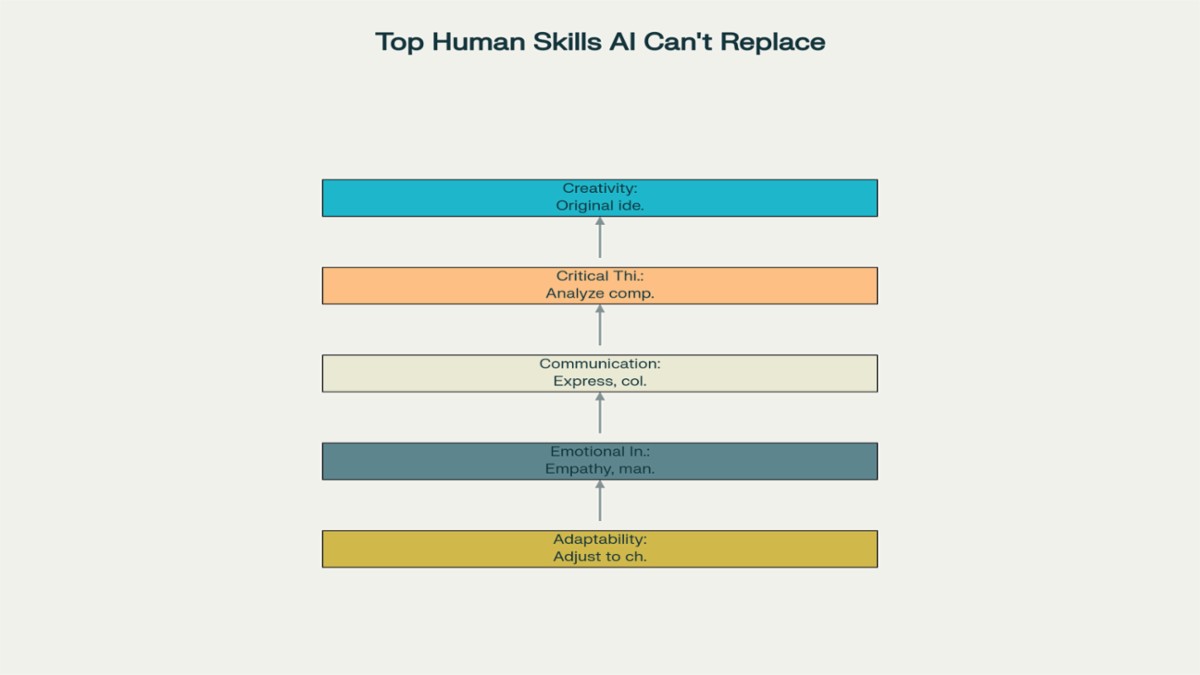
While AI can automate many functions, certain skills remain uniquely human—and highly valuable. Employers increasingly seek individuals who can:
-
Adapt to Technological Change: Rapid learning and digital literacy are crucial as tools evolve.
-
Critical Thinking & Problem Solving: While AI excels at pattern recognition, humans outperform in complex, context-driven analysis.
-
Emotional Intelligence & Communication: AI can process language but lacks the depth of human empathy and interpersonal skills.
-
Creativity and Innovation: Original ideas, artistic creation, and out-of-the-box thinking distinguish humans from machines.
-
Collaboration and Leadership: Coordinating teams, resolving conflicts, and inspiring others remain human domains.
Expert Perspectives
Industry leaders emphasize continuous learning as the best defense against obsolescence.
“Workers who combine technical proficiency with creative and interpersonal skills will be indispensable in tomorrow’s AI-driven economy.”
— Dr. Aya Rodriguez, Future of Work Analyst
Furthermore, the World Economic Forum named “analytical thinking, complex problem-solving, and adaptability” as top skills for 2025. Career coaches also recommend developing proficiency with AI tools—not just resisting them—so that you can leverage technology to amplify your own contributions.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the automation of certain positions may seem daunting, AI opens up new job categories. For example:
-
AI System Trainers (teaching AI systems through human feedback)
-
Data Annotation Specialists
-
AI Ethics Consultants
-
Human-AI Collaboration Managers
However, the transition will require reskilling and support for workers whose roles are most exposed to automation. Governments and organizations must invest in upskilling programs to ensure equitable access to new opportunities.
What's Next? A Call for Proactive Adaptation
Complacency is not an option in the AI era. Individuals who stay informed, embrace lifelong learning, and proactively build relevant skills will be best positioned to thrive. Now is the time to evaluate your current capabilities and seek growth in areas where humans have a clear edge over automation.
Conclusion & Outlook
As AI rapidly transforms the job market, those who adapt by cultivating uniquely human skills—creativity, critical thinking, emotional intelligence, and the ability to collaborate—will future-proof their careers. Investing in these strengths, along with technical proficiency, will ensure long-term relevance in an ever-changing workplace defined by AI.

Comments